The United Nations General Assembly adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015, as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. The SDGs aim to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure peace and prosperity for all.
The SDGs provide a holistic framework for addressing some of the world’s most urgent issues, including inequality, poverty, climate change, and environmental degradation. They take a comprehensive approach to sustainable development, understanding that social, economic, and environmental concerns are linked and must be addressed simultaneously.

The key feature of the SDGs is their inclusiveness, ensuring that sustainable development is achieved for all, regardless of their race, gender, or socioeconomic status. The SDGs also encourage partnerships between governments, businesses, and civil society organizations, recognizing that sustainable development cannot be achieved by any one sector working in isolation.
In order to achieve the SDGs, it is essential to mobilize the resources and political will necessary to implement them. This necessitates a multi-stakeholder strategy in which governments, the commercial sector, civil society, and people collaborate to accomplish common goals. It also requires a more integrated and coordinated approach to development, in which economic, social, and environmental dimensions are considered in a holistic and complementary manner.
The government has taken several steps to deliver the promise of fulfillment of SDGs and improve the lives of the citizens. One of the primary goals of the SDGs is to end poverty in all its forms. India has made significant progress in reducing poverty levels in the country. The number of people living below the poverty line has fallen from 21.9% in 2011 to 6.7% in 2019. This is a remarkable achievement, given that India is home to 17.5% of the world’s population. Financial inclusion is another important goal of the SDGs. The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana has been successful in providing access to banking services to millions of people, particularly in rural and unbanked areas. This has helped improve financial stability and economic independence for many families in the country. Also, ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all is another goal of the SDGs. The Ayushman Bharat initiative launched by the government has provided health insurance coverage to over 50 crore people, helping to improve access to quality healthcare in the country.
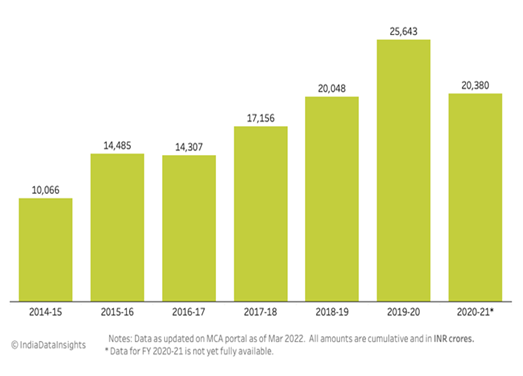
Apart from the government, the corporate sector is also playing an important role through their CSR activities. Companies are adopting sustainable business models that focus on reducing their environmental impact and ensuring social responsibility. This includes reducing waste, reducing carbon emissions, and adopting renewable energy sources. By doing so, companies are not only contributing to the achievement of SDGs but also creating long-term value for their businesses. Companies are also promoting inclusion, providing opportunities to underrepresented groups and creating a diverse and inclusive workplace. This helps to address issues of inequality and contributes to the achievement of SDGs. Many campaigns and initiatives are being taken up by the companies under CSR expenditure and the amount has been increasing over the years. These corporations also tie up with NGOs for their CSR activities. For example, TATA Steel and Plan India, HUL and WaterAid, Wipro and Smile Foundation etc.
NGOs, as independent actors with a long history of engagement in development issues, bring a unique set of skills, knowledge, and resources to the table. One of the key roles of NGOs in the implementation of the SDGs is advocacy. NGOs play an important role in raising awareness and advocating for the SDGs at the national and local level. They can mobilize public opinion and provide a voice for marginalized groups and communities, and engage in advocacy to promote the integration of the SDGs into national development strategies and policies.
They also play a key role in implementing the SDGs at the grassroots level. They have extensive networks and a presence in communities, and are well positioned to deliver services, support local initiatives, and build capacities. NGOs can provide essential services, such as health care and education, and can play a key role in the development of local economies, particularly in rural areas.
Khwaahish is one such NGO supporting the cause of introducing SDGs. The goals in focus for the NGO are: Goal 2 (Zero Hunger), Goal 3 (Good health and well-being), Goal 4 (Quality Education), Goal 5 (Gender Equality), Goal 6 (Clean water and Sanitation), Goal 10 (Reduced Inequalities) and Goal 17 (Partnerships for the Goals). The NGO is covering these SDGs mainly through 4 projects:
- Project Neev – Education
- Project Aarogyam – Health
- Project Sampoorna – Skill
- Project SARA – Compassion
Although, there is a long way to go for the nation to achieve sustainable development in its glory, Khwaahish hopes to contribute towards the progress made so far for a brighter and more sustainable future for all.
